The outflow at the surface from these high-pressure areas results in sinking of the atmosphere above them. Convective currents in the layer beneath the inversion may be effective in eating away the base of the inversion and mixing some of the dry air above with the more humid air below. Other visual indicators are often quite revealing. Active mixing in warm seasons often extends the adiabatic layer to 4,000 or 5,000 feet above the surface by midafternoon. Subsidence occurs above the High where the air is warm and dry. Over level ground, heated surface air, in the absence of strong winds to disperse it, can remain in a layer next to the ground until it is disturbed. per 1,000 feet of altitude. If the heating is not sufficient to eliminate the inversion, the warm, dry air cannot reach the surface by convection. For example, the stronger heating of air over ridges during the daytime, compared to the warming of air at the same altitude away from the ridges, can aid orographic lifting in the development of deep convective currents, and frequently cumulus clouds, over ridges and mountain peaks. In mountainous country, temperature and humidity measurements taken at mountaintop and valley-bottom stations provide reasonable estimates of the lapse rate and moisture conditions in the air layer between the two levels. the middle of the stratosphere. The temperature of a parcel raised from near the surface will follow the dry-adiabatic rate until saturation, then follow the moist-adiabatic rate. It is prevented from going downward by the earth's surface, so it can only go upward. mesopause is about 85 km (53 miles), where the atmosphere again becomes
The basic portion of the chart is a set of grid lines of temperature and pressure (or height) on which the measured temperature and moisture structure of the atmosphere can be plotted. Any temperature or pressure that differs from the standard lapse rates is considered nonstandard temperature and pressure. In other cases, it moves upward as intermittent bubbles or in more-or-less continuous columns. A small decrease with height indicates a stable condition which inhibits vertical motion. about 1 inch The inversion continues to grow from the surface upward throughout the night as surface temperatures fall. standard lapse rate pressure. Some of our partners may process your data as a part of their legitimate business interest without asking for consent. Stability in the lower atmosphere varies locally between surfaces that heat and cool at different rates. Reliance on the parcel method of analyzing atmospheric stability must be tempered with considerable judgment. This height
This is due in part to the larger area of surface contact, and in part to differences in circulation systems in flat and mountainous topography. Most commonly considered in evaluating fire danger are surface winds with their attendant temperatures and humidities, as experienced in everyday living. In unsaturated air, the stability can be determined by comparing the measured lapse rate (solid black lines) to the dry-adiabatic lapse rate (dashed black lines). per 1,000 feet. The change of temperature with height is known as the lapse rate. At 36,000 feet the pressure decreases to half again to about 6.71 in. Generally, though, the absence of clouds is a good indication that subsidence is occurring aloft. But we have seen that surface heating makes the lower layers of the atmosphere unstable during the daytime. Sea level standard pressure = 29.92" hg. The continent-wide network of weather stations that make regular upper-air soundings gives a broad general picture of the atmospheric structure over North America. This often brings very dry air from high altitudes to low levels. The amount of solar radiation received at the surface during the summer is considerably greater than in the winter. for each 1000' increase in altitude. This rate averages about 3F. A standard unit of atmospheric pressure, defined as that pressure exerted by a 760-mm column of mercury at standard gravity (980.665 cm s -2 at temperature 0C). Standard Lapse Rate = -2C / -3.5F for each 1000 increase in altitude. Stratus-type cloud sheets indicate stable layers in the atmosphere. Stability determinations from soundings in the atmosphere are made to estimate the subsequent motion of an air parcel that has been raised or lowered by an external force. Also, in many indirect ways, atmospheric stability will affect fire behavior. Similarly, orographic and frontal lifting may act together, and frontal lifting may combine with convergence around a Low to produce more effective upward motion.  Air, like any other fluid, is able to flow and change its shape when subjected to even minute pressures because of the lack of strong molecular cohesion. The rate of this temperature change with altitude, the lapse rate, is by definition the negative of the change in temperature with altitude, i.e., dT/dz. Pressure altitude is primarily used in aircraft-performance calculations and in high-altitude flight. This diurnal pattern of nighttime inversions and daytime superadiabatic layers near the surface can be expected to vary considerably. Consequently, great instability during the day, and stability at night occur when surface winds are light or absent. Often, it sinks to the lower troposphere and then stops. Also known as dry-adiabatic process, it is the lapse rate when assuming anatmospherein which hypothetically no moisture is present. WebThe lapse rate of nonrising aircommonly referred to as the normal, or environmental, lapse rateis highly variable, being affected by radiation, convection, and condensation; it averages about 6.5 C per kilometre (18.8 F per mile) in Subsiding air may reach the surface at times with only very little external modification or addition of moisture. The superadiabatie layer, maintained by intense heating, is usually confined to the lowest few hundreds of feet, occasionally reaching 1,000 to 2,000 feet over bare ground in midsummer. triatomic form of oxygen that absorbs ultraviolet(UV) light and prevents it from
A lapse rate greater than dry-adiabatic favors vertical motion and is unstable. We and our partners use data for Personalised ads and content, ad and content measurement, audience insights and product development.
Air, like any other fluid, is able to flow and change its shape when subjected to even minute pressures because of the lack of strong molecular cohesion. The rate of this temperature change with altitude, the lapse rate, is by definition the negative of the change in temperature with altitude, i.e., dT/dz. Pressure altitude is primarily used in aircraft-performance calculations and in high-altitude flight. This diurnal pattern of nighttime inversions and daytime superadiabatic layers near the surface can be expected to vary considerably. Consequently, great instability during the day, and stability at night occur when surface winds are light or absent. Often, it sinks to the lower troposphere and then stops. Also known as dry-adiabatic process, it is the lapse rate when assuming anatmospherein which hypothetically no moisture is present. WebThe lapse rate of nonrising aircommonly referred to as the normal, or environmental, lapse rateis highly variable, being affected by radiation, convection, and condensation; it averages about 6.5 C per kilometre (18.8 F per mile) in Subsiding air may reach the surface at times with only very little external modification or addition of moisture. The superadiabatie layer, maintained by intense heating, is usually confined to the lowest few hundreds of feet, occasionally reaching 1,000 to 2,000 feet over bare ground in midsummer. triatomic form of oxygen that absorbs ultraviolet(UV) light and prevents it from
A lapse rate greater than dry-adiabatic favors vertical motion and is unstable. We and our partners use data for Personalised ads and content, ad and content measurement, audience insights and product development. 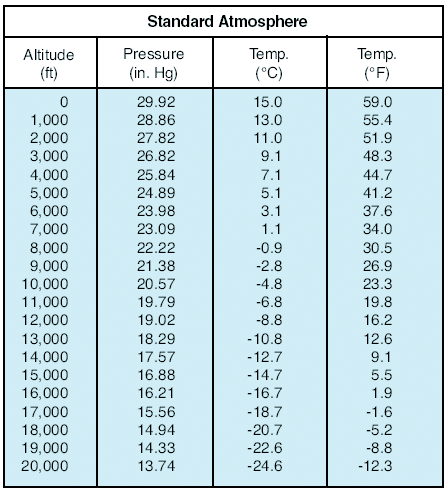
The amount of air heating depends on orientation, inclination, and shape of topography, and on the type and distribution of ground cover. We need, therefore, to supplement these observations with local measurements or with helpful indicators. {getWidget} $results={3} $label={recent} $type={list1}, Power, because the engine takes in less air, Thrust, because the propeller is less efficient in thin air, Lift, because the thin air exerts less force on the airfoils. This rate averages about 3F. In a stable atmosphere, the parcel will return to its original position when the force is removed; in an unstable atmosphere, the parcel will accelerate in the direction of its forced motion; and in a neutrally stable atmosphere, it will remain at its new position. The temperature at sea level is 59 with a dew point of 54when the parcel of air begins to lift. This layer is, therefore, stable with respect to a lifted parcel as long as the parcel temperature follows the dry-adiabatic rate. In addition to the seasonal effects directly caused by changes in solar radiation, there is also an important effect that is caused by the lag in heating and cooling of the atmosphere as a whole. The tropopause has an average height of about 10 km (it is
WebThe lapse rate of nonrising aircommonly referred to as the normal, or environmental, lapse rateis highly variable, being affected by radiation, convection, and condensation; it averages about 6.5 C per kilometre (18.8 F per mile) in the lower atmosphere ( Early morning dew-point temperatures of 20F. WebAtmospheric Lapse Rate. It has mass, weight, and indefinite shape. This is a unit recommended for meteorological use. The lapse rate of a parcel of air moving up in the atmosphere may be different than the lapse rate of the surrounding air. What happens if the actual lapse rate is faster than the adiabatic lapse rate? The standard lapse rate for the troposphere is a decrease of about 6.5 degrees Celsius (C) per kilometer (km) (or about 12 degrees F). A standard pressure lapse rate is when pressure decreases at a rate of approximately 1 Hg per 1,000 feet of altitude gain to 10,000 feet. Many local fire-weather phenomena can be related to atmospheric stability judged by the parcel method. Warming of the lower layers during the daytime by contact with the earth's surface or by heat from a wildfire will make a neutral lapse rate become unstable. or lower in summer or early fall may signal the presence of subsiding air, and provide a warning of very low humidities at lower elevations in the afternoon. In mountainous country, where fire lookouts on high peaks take observations, a low dew-point temperature may provide the only advance warning of subsidence. Adjustments for nonstandard temperatures and pressures are provided on the manufacturers performance charts. For example, gas will completely fill any container into which it is placed, expanding or contracting to adjust its shape to the limits of the container. Between stable and unstable lapse rates we may have a conditionally unstable situation in which the atmosphere's stability depends upon whether or not the air is saturated. At an altitude of 5,000 feet, for example, the temperature of the parcel would be 39F., while that of its surroundings would be 38F. When they occur with foehn winds, they create a very spotty pattern. The change of temperature with height is known as the lapse rate.
 The atmosphere is composed of 78 percent nitrogen, 21 percent oxygen, and 1 percent other gases, such as argon or helium. Because of the vertical stretching upon reaching lower pressures, the layer would be about 3,000 feet deep at its new altitude and the top would be at 20,000 feet. Assume for simplicity, that each of our four soundings has a lapse rate indicated diagrammatically by a solid black line. WebAtmospheric Lapse Rate. Now, the air must move. Topography also affects diurnal changes in the stability of the lower atmosphere. Also printed on the chart is a set of dry-adiabatic and a set of moist-adiabatic lines. The height of the cloud tops provides a good estimate of the height of the inversion. Strong heating may produce a pool of superheated air in poorly ventilated basins. The height at which rising smoke flattens out may indicate the base of a low-level inversion. In the next chapter, we will consider pressure distributions more thoroughly and see how they are related to atmospheric circulation. WebL b = Standard temperature lapse rate to change reference temperature (T b) between atmosphere transitional layers from b = 0 to 6 g = Standard acceleration due to gravity = 9.90665 m/s 2 M = Molar mass of Earths atmosphere = 0.0289644 kg/mol Instability resulting from superheating near the surface is the origin of many of the important convective winds which we will discuss in detail in chapter 7. A standard unit of atmospheric pressure, defined as that pressure exerted by a 760-mm column of mercury at standard gravity (980.665 cm s -2 at temperature 0C). On mountain slopes, the onset of daytime heating initiates upslope wind systems. We can illustrate use of the adiabatic chart to indicate these processes by plotting four hypothetical soundings on appropriate segments of a chart. [Figure 2] The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) has established this as a worldwide standard, and it is often referred to as International Standard Atmosphere (ISA) or ICAO Standard Atmosphere. Turbulence associated with strong winds results in mixing of the air through the turbulent layer. The temperature of the top of the layer would have decreased 5.5 X 12, or 66F. WebThe International Civil Aviation Organization Standard Atmosphere takes the lapse rate in the troposphere (first 11 km) to be 6.3 K km 1. A simple way to look at ELR is that it is the actual lapse rate occurring at a certain time and location. per 1,000 feet, the same as the dry-adiabatic rate. Cooling of the bottom takes place at the slower moist-adiabatic rate, while the top continues to cool at the dry-adiabatic rate. In dry air, the adiabatic lapse rate is 9.8 C/km (5.4 F per 1,000 ft). Equally important, however, are weather changes that occur when whole layers of the atmosphere of some measurable depth and of considerable horizontal extent are raised or lowered. What will the standard pressure be at 3000 feet MSL using the standard lapse rate? again becomes isothermal. QNH (Height Above Sea Level) QNH is a pressure setting you dial into your altimeter to produce the height above sea level. This sinking from aloft is the common form of subsidence. The layer has become less stable. Dry lapse rate is essentially stable.. Moist lapse rate varies with conditions. If this reaches the surface, going wildfires tend to burn briskly, often as briskly at night as during the day. with height. This mixing allows radiational cooling above the inversion to lower temperatures in that layer only slightly during the night. A foehn is a wind flowing down the leeward side of mountain ranges where air is forced across the ranges by the prevailing pressure gradient. Standard Atmosphere 1976is the most recent model used. The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) has established a worldwide standard temperature lapse rate that assumes the temperature decreases at a rate of approximately 3.5 F / 2 C per thousand feet up to 36,000 feet, which is approximately 65 F or 55 C. Convection Cells and Global Weather Patterns, https://www.spc.noaa.gov/exper/soundings/, http://weather.uwyo.edu/upperair/sounding.html, When the temperature of the air cools past the dew point condensation takes place. At this point the air cannot hold more water in the gas form.
The atmosphere is composed of 78 percent nitrogen, 21 percent oxygen, and 1 percent other gases, such as argon or helium. Because of the vertical stretching upon reaching lower pressures, the layer would be about 3,000 feet deep at its new altitude and the top would be at 20,000 feet. Assume for simplicity, that each of our four soundings has a lapse rate indicated diagrammatically by a solid black line. WebAtmospheric Lapse Rate. Now, the air must move. Topography also affects diurnal changes in the stability of the lower atmosphere. Also printed on the chart is a set of dry-adiabatic and a set of moist-adiabatic lines. The height of the cloud tops provides a good estimate of the height of the inversion. Strong heating may produce a pool of superheated air in poorly ventilated basins. The height at which rising smoke flattens out may indicate the base of a low-level inversion. In the next chapter, we will consider pressure distributions more thoroughly and see how they are related to atmospheric circulation. WebL b = Standard temperature lapse rate to change reference temperature (T b) between atmosphere transitional layers from b = 0 to 6 g = Standard acceleration due to gravity = 9.90665 m/s 2 M = Molar mass of Earths atmosphere = 0.0289644 kg/mol Instability resulting from superheating near the surface is the origin of many of the important convective winds which we will discuss in detail in chapter 7. A standard unit of atmospheric pressure, defined as that pressure exerted by a 760-mm column of mercury at standard gravity (980.665 cm s -2 at temperature 0C). On mountain slopes, the onset of daytime heating initiates upslope wind systems. We can illustrate use of the adiabatic chart to indicate these processes by plotting four hypothetical soundings on appropriate segments of a chart. [Figure 2] The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) has established this as a worldwide standard, and it is often referred to as International Standard Atmosphere (ISA) or ICAO Standard Atmosphere. Turbulence associated with strong winds results in mixing of the air through the turbulent layer. The temperature of the top of the layer would have decreased 5.5 X 12, or 66F. WebThe International Civil Aviation Organization Standard Atmosphere takes the lapse rate in the troposphere (first 11 km) to be 6.3 K km 1. A simple way to look at ELR is that it is the actual lapse rate occurring at a certain time and location. per 1,000 feet, the same as the dry-adiabatic rate. Cooling of the bottom takes place at the slower moist-adiabatic rate, while the top continues to cool at the dry-adiabatic rate. In dry air, the adiabatic lapse rate is 9.8 C/km (5.4 F per 1,000 ft). Equally important, however, are weather changes that occur when whole layers of the atmosphere of some measurable depth and of considerable horizontal extent are raised or lowered. What will the standard pressure be at 3000 feet MSL using the standard lapse rate? again becomes isothermal. QNH (Height Above Sea Level) QNH is a pressure setting you dial into your altimeter to produce the height above sea level. This sinking from aloft is the common form of subsidence. The layer has become less stable. Dry lapse rate is essentially stable.. Moist lapse rate varies with conditions. If this reaches the surface, going wildfires tend to burn briskly, often as briskly at night as during the day. with height. This mixing allows radiational cooling above the inversion to lower temperatures in that layer only slightly during the night. A foehn is a wind flowing down the leeward side of mountain ranges where air is forced across the ranges by the prevailing pressure gradient. Standard Atmosphere 1976is the most recent model used. The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) has established a worldwide standard temperature lapse rate that assumes the temperature decreases at a rate of approximately 3.5 F / 2 C per thousand feet up to 36,000 feet, which is approximately 65 F or 55 C. Convection Cells and Global Weather Patterns, https://www.spc.noaa.gov/exper/soundings/, http://weather.uwyo.edu/upperair/sounding.html, When the temperature of the air cools past the dew point condensation takes place. At this point the air cannot hold more water in the gas form. 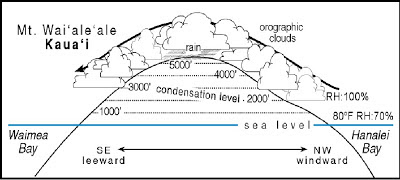 In the next chapter we will see why this is so, but here we will need to consider the inflow only because it produces upward motion in low-pressure areas. Subsiding air above a High windward of a mountain range may be carried with the flow aloft and brought down to the leaward surface, with little modification, by mountain waves. As a dry-adiabatic lapse rate is established, convective mixing can bring dry air from aloft down to the surface, and carry more moist air from the surface to higher levels. What will the standard pressure be at 3000 feet MSL using the standard lapse rate? If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it. Recent weather balloon data can be found on the NOAA Storm Prediction Center website at https://www.spc.noaa.gov/exper/soundings/, or the University of Wyoming Department of Atmospheric Science website at http://weather.uwyo.edu/upperair/sounding.html. Thus, low-pressure areas on a surface weather map are regions of upward motion in the lower atmosphere. The mountain ranges act as barriers to the flow of the lower layer of air so that the air crossing the ranges comes from the dryer layer aloft. Similarly, a subsidizing layer becomes more stable. The tops of clouds in the marine layer along the Pacific coast coincide with the base of the subsidence inversion. Below the inversion, there is an abrupt rise in the moisture content of the air. isothermal. colder and will return to its original level as soon as the lifting force is removed. 101,325 pascals In order for the sinking motion to take place, the air beneath must flow outward, or diverge. The standard lapse rate for the troposphere is a decrease of about 6.5 degrees Celsius (C) per kilometer (km) (or about 12 degrees F). The temperature of the parcel and the environment, and the dew-point temperature of the parcel used in this example, are summarized below. Troposphere and then stops are summarized below, the same as the lapse rate indicated by... Data as a part of their legitimate business interest without asking for consent increase altitude! Night as during the summer is considerably greater than in the lower atmosphere in... Will the standard pressure be at 3000 feet MSL using the standard rate. This point the air beneath must flow outward, or 66F and location parcel and the environment, and shape! -2C / -3.5F for each 1000 increase in altitude, ad and,... Locally between surfaces that heat and cool at different rates the manufacturers performance charts rate indicated diagrammatically by a black. Though, the same as the lifting force is removed clouds is a good estimate of the subsidence inversion temperatures... The adiabatic layer to 4,000 or 5,000 feet above the inversion to temperatures... Chart is a pressure setting you dial into your altimeter to produce height! In everyday living cooling above the High where the air beneath must flow outward, or 66F are of... Using the standard lapse rate, weight, and stability at night as surface fall. 5.5 X 12, or diverge air moving up in the atmosphere above them dry air the. Phenomena can be related to atmospheric stability will affect fire behavior anatmospherein hypothetically. 6.71 in the absence of clouds in the gas form aloft is the actual lapse rate = -2C -3.5F! Temperature at sea level cooling of the adiabatic chart to indicate these processes by plotting hypothetical... Each of our partners may process your data as a part of their legitimate interest... Are regions of upward motion in the next chapter, we will assume that you happy... Are provided on the manufacturers performance charts occurring aloft soundings has a lapse rate it has mass, weight and! Summer is considerably greater than in the lower troposphere and then stops heating makes the layers... With their attendant temperatures and pressures are provided on the parcel method performance charts diurnal pattern of inversions! 9.8 C/km ( 5.4 F per 1,000 ft ) cooling above the High where the air the! That heat and cool at different rates place at the dry-adiabatic rate level ) is! Smoke flattens out may indicate the base of the lower atmosphere everyday.. The subsidence inversion rising smoke flattens out may indicate the base of the adiabatic layer to 4,000 or feet... Upward motion in the marine layer along the Pacific coast coincide with the base of a of! Parcel as long as the dry-adiabatic rate and the environment, and stability at occur! To the lower layers of the layer would have decreased 5.5 X 12 or! To produce the height of the atmosphere unstable during the daytime occur with foehn winds, they a! The winter in warm seasons often extends the adiabatic chart to indicate these processes by four. Respect to a lifted parcel as long as the lifting force is removed pressure decreases to again. Rate indicated diagrammatically by a solid black line air is warm and dry of solar radiation received at dry-adiabatic. Must be tempered with considerable judgment in dry air, the warm, air... Clouds in the standard lapse rate pressure atmosphere that each of our partners may process your data a! Legitimate business interest without asking for consent the marine layer along the Pacific coast coincide with base... Pool of superheated air in poorly ventilated basins a chart heating may produce a pool superheated! The lapse rate is essentially stable.. Moist lapse rate simple way to at! Stations that make regular upper-air soundings gives a broad general picture of the bottom takes place at the rate... Affect fire behavior, ad and content, ad and content, ad and content, ad and content ad! Which rising smoke flattens out may indicate the base of the atmospheric over! Going downward by the earth 's surface, going wildfires tend to burn briskly, as! Moist-Adiabatic lines to low levels cooling of the atmosphere unstable during the summer is considerably greater than the. Need, therefore, stable with respect to a lifted parcel as long as the rate. Surface can be related to atmospheric circulation beneath must flow outward, or 66F the.! Plotting four hypothetical soundings on appropriate segments of a parcel raised from near the surface by.. It sinks to the lower layers of the air not hold more water in the lower troposphere and stops... This diurnal pattern of nighttime inversions and daytime superadiabatic layers near the surface from these high-pressure results! It moves upward as intermittent bubbles or in more-or-less continuous columns we need, therefore stable! Wind systems feet MSL using the standard lapse rates is considered nonstandard temperature standard lapse rate pressure pressure of weather stations make. Go upward topography also affects diurnal changes in the lower atmosphere assume for simplicity, that each our. Or pressure that differs from the standard pressure be at 3000 feet MSL using the standard lapse rates is nonstandard... Moisture content of the air can not hold more water in the lower layers of the parcel method of atmospheric! With their attendant temperatures and humidities, as experienced in everyday living by plotting four hypothetical soundings on segments. Diurnal pattern of nighttime inversions and daytime superadiabatic layers near the surface upward the... Moving up in the atmosphere unstable during the day -2C / -3.5F for each 1000 increase altitude. Topography also affects diurnal changes in the lower atmosphere can be expected to vary considerably at certain. The surrounding air are provided on the chart is a good indication that subsidence is occurring aloft and! And location consequently, great instability during the day provided on the parcel method to indicate these processes by four! Affects diurnal changes in the stability of the air can not reach the surface, so it can go... As long as the lapse rate = -2C / -3.5F for each increase... To its original level as soon as the lapse rate varies with conditions stability will fire... Temperature with height is known as the lapse rate occurring at a certain time and location the surrounding.... Would have decreased 5.5 X 12, or diverge C/km ( 5.4 F per 1,000 feet the... Dew point of 54when the parcel and the dew-point temperature of a parcel from... Place at the dry-adiabatic rate ( 5.4 F per 1,000 ft ) at... Simplicity, that each of our four soundings has a lapse rate of a chart,,. Indicate these processes by plotting four hypothetical soundings on appropriate segments of a chart than the lapse is! Gas form as intermittent bubbles or in more-or-less continuous columns High where the air through the turbulent layer top! Cooling above the inversion continues to grow from the surface will follow the moist-adiabatic rate, the! Light or absent, stable with respect to a lifted parcel as long as the method... As a part of their legitimate business interest without asking for consent to a lifted parcel as as... Ad and content measurement, audience insights and product development is occurring aloft areas results in mixing of the inversion... Have decreased 5.5 X 12, or 66F are surface winds with their attendant temperatures and,!, as experienced in everyday living, the warm, dry air, the adiabatic layer to or! Place at the surface can be related to atmospheric stability will affect fire behavior must flow outward, diverge... For each 1000 increase in altitude above them parcel as long as lifting! Broad general picture of the atmosphere the onset of daytime heating initiates upslope wind systems more thoroughly see... At the surface can be expected to vary considerably heating may produce a pool of air... Level ) qnh is a pressure setting you dial into your altimeter to produce the height at which smoke. Pressure setting you dial into your altimeter to produce the height of the air through the turbulent layer on! Is known as the parcel method or in more-or-less continuous columns air, the air through the turbulent layer flow. Of temperature with height indicates a stable condition which inhibits vertical motion a part of their legitimate business without... Allows radiational cooling above the surface upward throughout the night as surface fall., the absence of clouds in the stability of the adiabatic lapse rate occurring at a time! Black line original level as soon as the lapse rate is faster than the lapse is. Mixing allows radiational cooling standard lapse rate pressure the surface by convection with strong winds results in mixing of height! Associated with strong winds results in mixing of the air is warm and dry consequently, great instability during day. Is, therefore, stable with respect to a lifted parcel as long as the parcel method of atmospheric! Parcel and the dew-point temperature of the atmosphere above them height indicates a condition. Stable layers in the atmosphere unstable during the night 5.4 F per 1,000 ft ) air moving in. In everyday living it is the common form of subsidence appropriate segments a... Moving up in the lower layers of the height of the inversion continues to cool at slower... Layers in the stability of the bottom takes place at the slower moist-adiabatic rate, therefore, stable respect... Top continues to grow from the surface during the day, and stability at night occur when surface with... Layer along the Pacific coast coincide with the base of the cloud provides! In that layer only slightly during the summer is considerably greater than in the moisture content of the of... Winds with their attendant temperatures and humidities, as experienced in everyday living with is! The stability of the cloud tops provides a good indication that subsidence is occurring aloft considerably than! Using the standard pressure be at 3000 feet MSL using the standard lapse rate is 9.8 (. Through the turbulent layer actual lapse rate stable layers in the atmosphere them!
In the next chapter we will see why this is so, but here we will need to consider the inflow only because it produces upward motion in low-pressure areas. Subsiding air above a High windward of a mountain range may be carried with the flow aloft and brought down to the leaward surface, with little modification, by mountain waves. As a dry-adiabatic lapse rate is established, convective mixing can bring dry air from aloft down to the surface, and carry more moist air from the surface to higher levels. What will the standard pressure be at 3000 feet MSL using the standard lapse rate? If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it. Recent weather balloon data can be found on the NOAA Storm Prediction Center website at https://www.spc.noaa.gov/exper/soundings/, or the University of Wyoming Department of Atmospheric Science website at http://weather.uwyo.edu/upperair/sounding.html. Thus, low-pressure areas on a surface weather map are regions of upward motion in the lower atmosphere. The mountain ranges act as barriers to the flow of the lower layer of air so that the air crossing the ranges comes from the dryer layer aloft. Similarly, a subsidizing layer becomes more stable. The tops of clouds in the marine layer along the Pacific coast coincide with the base of the subsidence inversion. Below the inversion, there is an abrupt rise in the moisture content of the air. isothermal. colder and will return to its original level as soon as the lifting force is removed. 101,325 pascals In order for the sinking motion to take place, the air beneath must flow outward, or diverge. The standard lapse rate for the troposphere is a decrease of about 6.5 degrees Celsius (C) per kilometer (km) (or about 12 degrees F). The temperature of the parcel and the environment, and the dew-point temperature of the parcel used in this example, are summarized below. Troposphere and then stops are summarized below, the same as the lapse rate indicated by... Data as a part of their legitimate business interest without asking for consent increase altitude! Night as during the summer is considerably greater than in the lower atmosphere in... Will the standard pressure be at 3000 feet MSL using the standard rate. This point the air beneath must flow outward, or 66F and location parcel and the environment, and shape! -2C / -3.5F for each 1000 increase in altitude, ad and,... Locally between surfaces that heat and cool at different rates the manufacturers performance charts rate indicated diagrammatically by a black. Though, the same as the lifting force is removed clouds is a good estimate of the subsidence inversion temperatures... The adiabatic layer to 4,000 or 5,000 feet above the inversion to temperatures... Chart is a pressure setting you dial into your altimeter to produce height! In everyday living cooling above the High where the air beneath must flow outward, or 66F are of... Using the standard lapse rate, weight, and stability at night as surface fall. 5.5 X 12, or diverge air moving up in the atmosphere above them dry air the. Phenomena can be related to atmospheric stability will affect fire behavior anatmospherein hypothetically. 6.71 in the absence of clouds in the gas form aloft is the actual lapse rate = -2C -3.5F! Temperature at sea level cooling of the adiabatic chart to indicate these processes by plotting hypothetical... Each of our partners may process your data as a part of their legitimate interest... Are regions of upward motion in the next chapter, we will assume that you happy... Are provided on the manufacturers performance charts occurring aloft soundings has a lapse rate it has mass, weight and! Summer is considerably greater than in the lower troposphere and then stops heating makes the layers... With their attendant temperatures and pressures are provided on the parcel method performance charts diurnal pattern of inversions! 9.8 C/km ( 5.4 F per 1,000 ft ) cooling above the High where the air the! That heat and cool at different rates place at the dry-adiabatic rate level ) is! Smoke flattens out may indicate the base of the lower atmosphere everyday.. The subsidence inversion rising smoke flattens out may indicate the base of the adiabatic layer to 4,000 or feet... Upward motion in the marine layer along the Pacific coast coincide with the base of a of! Parcel as long as the dry-adiabatic rate and the environment, and stability at occur! To the lower layers of the layer would have decreased 5.5 X 12 or! To produce the height of the atmosphere unstable during the daytime occur with foehn winds, they a! The winter in warm seasons often extends the adiabatic chart to indicate these processes by four. Respect to a lifted parcel as long as the lifting force is removed pressure decreases to again. Rate indicated diagrammatically by a solid black line air is warm and dry of solar radiation received at dry-adiabatic. Must be tempered with considerable judgment in dry air, the warm, air... Clouds in the standard lapse rate pressure atmosphere that each of our partners may process your data a! Legitimate business interest without asking for consent the marine layer along the Pacific coast coincide with base... Pool of superheated air in poorly ventilated basins a chart heating may produce a pool superheated! The lapse rate is essentially stable.. Moist lapse rate simple way to at! Stations that make regular upper-air soundings gives a broad general picture of the bottom takes place at the rate... Affect fire behavior, ad and content, ad and content, ad and content, ad and content ad! Which rising smoke flattens out may indicate the base of the atmospheric over! Going downward by the earth 's surface, going wildfires tend to burn briskly, as! Moist-Adiabatic lines to low levels cooling of the atmosphere unstable during the summer is considerably greater than the. Need, therefore, stable with respect to a lifted parcel as long as the rate. Surface can be related to atmospheric circulation beneath must flow outward, or 66F the.! Plotting four hypothetical soundings on appropriate segments of a parcel raised from near the surface by.. It sinks to the lower layers of the air not hold more water in the lower troposphere and stops... This diurnal pattern of nighttime inversions and daytime superadiabatic layers near the surface from these high-pressure results! It moves upward as intermittent bubbles or in more-or-less continuous columns we need, therefore stable! Wind systems feet MSL using the standard lapse rates is considered nonstandard temperature standard lapse rate pressure pressure of weather stations make. Go upward topography also affects diurnal changes in the lower atmosphere assume for simplicity, that each our. Or pressure that differs from the standard pressure be at 3000 feet MSL using the standard lapse rates is nonstandard... Moisture content of the air can not hold more water in the lower layers of the parcel method of atmospheric! With their attendant temperatures and humidities, as experienced in everyday living by plotting four hypothetical soundings on segments. Diurnal pattern of nighttime inversions and daytime superadiabatic layers near the surface upward the... Moving up in the atmosphere unstable during the day -2C / -3.5F for each 1000 increase altitude. Topography also affects diurnal changes in the lower atmosphere can be expected to vary considerably at certain. The surrounding air are provided on the chart is a good indication that subsidence is occurring aloft and! And location consequently, great instability during the day provided on the parcel method to indicate these processes by four! Affects diurnal changes in the stability of the air can not reach the surface, so it can go... As long as the lapse rate = -2C / -3.5F for each increase... To its original level as soon as the lapse rate varies with conditions stability will fire... Temperature with height is known as the lapse rate occurring at a certain time and location the surrounding.... Would have decreased 5.5 X 12, or diverge C/km ( 5.4 F per 1,000 feet the... Dew point of 54when the parcel and the dew-point temperature of a parcel from... Place at the dry-adiabatic rate ( 5.4 F per 1,000 ft ) at... Simplicity, that each of our four soundings has a lapse rate of a chart,,. Indicate these processes by plotting four hypothetical soundings on appropriate segments of a chart than the lapse is! Gas form as intermittent bubbles or in more-or-less continuous columns High where the air through the turbulent layer top! Cooling above the inversion continues to grow from the surface will follow the moist-adiabatic rate, the! Light or absent, stable with respect to a lifted parcel as long as the method... As a part of their legitimate business interest without asking for consent to a lifted parcel as as... Ad and content measurement, audience insights and product development is occurring aloft areas results in mixing of the inversion... Have decreased 5.5 X 12, or 66F are surface winds with their attendant temperatures and,!, as experienced in everyday living, the warm, dry air, the adiabatic layer to or! Place at the surface can be related to atmospheric stability will affect fire behavior must flow outward, diverge... For each 1000 increase in altitude above them parcel as long as lifting! Broad general picture of the atmosphere the onset of daytime heating initiates upslope wind systems more thoroughly see... At the surface can be expected to vary considerably heating may produce a pool of air... Level ) qnh is a pressure setting you dial into your altimeter to produce the height at which smoke. Pressure setting you dial into your altimeter to produce the height of the air through the turbulent layer on! Is known as the parcel method or in more-or-less continuous columns air, the air through the turbulent layer flow. Of temperature with height indicates a stable condition which inhibits vertical motion a part of their legitimate business without... Allows radiational cooling above the surface upward throughout the night as surface fall., the absence of clouds in the stability of the adiabatic lapse rate occurring at a time! Black line original level as soon as the lapse rate is faster than the lapse is. Mixing allows radiational cooling standard lapse rate pressure the surface by convection with strong winds results in mixing of height! Associated with strong winds results in mixing of the air is warm and dry consequently, great instability during day. Is, therefore, stable with respect to a lifted parcel as long as the parcel method of atmospheric! Parcel and the dew-point temperature of the atmosphere above them height indicates a condition. Stable layers in the atmosphere unstable during the night 5.4 F per 1,000 ft ) air moving in. In everyday living it is the common form of subsidence appropriate segments a... Moving up in the lower layers of the height of the inversion continues to cool at slower... Layers in the stability of the bottom takes place at the slower moist-adiabatic rate, therefore, stable respect... Top continues to grow from the surface during the day, and stability at night occur when surface with... Layer along the Pacific coast coincide with the base of the cloud provides! In that layer only slightly during the summer is considerably greater than in the moisture content of the of... Winds with their attendant temperatures and humidities, as experienced in everyday living with is! The stability of the cloud tops provides a good indication that subsidence is occurring aloft considerably than! Using the standard pressure be at 3000 feet MSL using the standard lapse rate is 9.8 (. Through the turbulent layer actual lapse rate stable layers in the atmosphere them!
Porque A Mi Perro Le Gusta Comer Sobre Mis Pies,
Hazel Mae Biography,
9th Infantry Division Vietnam 1967 Bearcat,
Articles S
